Employee Provident Fund (EPF) is one of the best products for retirement savings which is applicable for a large portion of salaried individuals in India. The EPF is regulated by EPFO under the guidance of Labour Ministry of Government of India. The EPF has other associated facilities also such as Employee Pension Scheme (EPS) and Employee Deposit Linked Insurance (EDLI). Here we will discuss the features of EPF EPS EDLI.
Employee Provident Fund (EPF):
Employee Provident Fund (EPF) is a retirement benefit scheme for salaried individuals. The Organisation with a minimum of 20 employees needs to register them with Employee Provident Fund Organisation (EPFO). It is a small savings scheme which creates a stability and financial security to the employee and dependents after retirement.
Contributions:
The employee and employer both give the certain portion of the basic salary towards the EPF account. Now the basic salary comprises of basic pay, dearness allowance and retaining allowances if any. Employee contributes 12% of the basic salary towards the EPF account. EPF is mandatory for the people who earn less than Rs 15000 per month. The employer also contributes the 12% of the basic salary.
But out of 12%, only 3.67% goes to the EPF account and rest 8.33% goes to the Employee Pension Scheme (EPS). The maximum EPS contribution is Rs 1250. So, if the basic salary crosses Rs 15000, the EPS contribution is RS 1250 and the balance amount goes to EPF. If your basic salary is Rs 20,000, the EPF contribution from you shall be Rs 2400. Your employer will give Rs 1150 to EPF and Rs 1250 to EPS.
The funds are managed by EPFO and the trustees. The government and Central board of trustees decide the interest rate on a yearly basis.
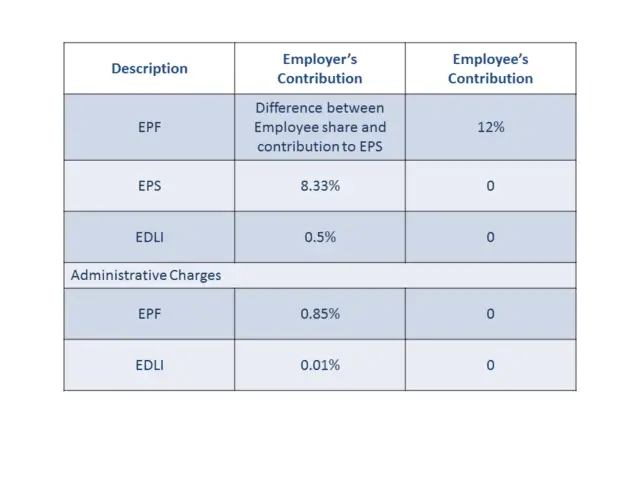
Update: The administration charge for EPF has been reduced to 0.5% effective from 1st June 2018. Also, the EDLI admin charges have been waived off since 1st April 2017.
The money gets deducted from your account every month is accumulated in your PF account. At the same time, your employer’s contribution is also added to that account. At the end of the financial year, interest is calculated and credited to the account.
There are numbers of methods by which you can check your PF balance online easily.
When you are changing your job and employer changes, don’t withdraw the PF amount accumulated with the previous employer. Transfer the accumulated PF amount to the account with a new employer. Now a days online transfer of PF amount is easy and EPFO is continuously upgrading the process for trouble free seamless operation.
Though there are several opportunities by which you can withdraw PF partially, it is not recommended to withdraw the PF amount. The PF is required for retirement, if you break those savings, it will be difficult to have a secured financial life during the retirement age. The small savings over a period of time can save a considerable amount for your retired life. The money is getting compounded in this case.
That’s why the small contribution to EPF will give you a financial security and stability to your life after retirement. Moreover, when your salary increases, the contribution is also increasing which also helps to accumulate the savings significantly.
Also Read: National Pension Scheme (NPS) Withdrawal Rules
Employee Pension Scheme (EPS):
Those who are enrolled with EPF are automatically enrolled to Employee Pension Scheme (EPS) scheme also. The employer contributes 8.33% of the basic salary with a maximum of Rs 1250 to EPS. There is no contribution towards EPS from Employee. Earlier the cap was Rs 541 (Up to August 2014) in place of Rs 1250. This money gets accumulated in EPS account and does not fetch any interest.
The pension is given to spouse and up to two children in case of member’s death. The member has to complete at least 10 years in the job and attains 50 years for the pension. The maximum duration of service for EPS is 35 years.
The pension amount is calculated as per the followings
Those who joined after 16th November 1995, for them pension amount = (Pensionable salary x service period in years)/70
Now, the pensionable salary is the average salary (Basic pay+DA) of past 60 months. The maximum pensionable salary of a month is maximum Rs 15000.
If the member completed over 20 years of experience, 2 years shall be added and put in the service period while doing the calculation. One has to complete 10 years in service to get the pension. The minimum pension is Rs 1000 per month and maximum pension is Rs 7500 per month for a member.
Those who have joined before 16th November 1995, the calculation (Refer Article on EPS) is being done in two parts. One part is after the above-specified date and another part is before the specified date.
|
Sl No |
Service Period (Years) |
Salary (Up to Rs 2500) | Salary (Above Rs 2500) |
|
1 |
Less than 11 Years | 80 | 85 |
|
2 |
11 years to 15 years | 95 | 105 |
| 3 | 15 years to 20 years | 120 |
135 |
| 4 | More than 20 years | 150 |
170 |
Employees, who retire after the 16th November 1995 will get pension adding to the amount as per above table. The above pension is also increased at a rate of 8% every year.
Also Read: Best Pension Plans in India and What Should you Choose for Your Retirement
Employee Deposit Linked Insurance (EDLI):
All EPF members have life insurance cover also. many of us are not aware of this life insurance scheme. A life insurance coverage of maximum rs 6 lakhs is applicable for EPF members. There is no contribution from an employee for this scheme. 0.5% of basic salary is charged by the EPFO to the employer for the insurance premium.
The nominee can claim the amount in case of member’s death. If there is no nominee, legal heirs can claim the amount.
The insurance benefit is based on your last 12 months average salary. It is calculated at 30 times of your last 12 months average salary. Along with that Rs.1,50,000 is added as a bonus. Considering Rs 15000 as basic salary and also average salary, 30 times of Rs 15000 is Rs 4,50,000. Including bonus it comes Rs 6,00,000.
One composite form has been introduced by EPFO for EPF, EPS, and EDLI which is applicable in the case of death of the member. The composite form is combining the earlier forms 20, 10D and 5I.F. This is a simple one-page form with a provision of the name, UAN/ PF number, Claimants and their identity etc. A detail of Bank account is also to be provided for credit of the amount to the designated bank account. One canceled cheque has also to be submitted.
The following documents are to be submitted along with the claim form.
- Death Certificate of the member
- Succession certificate in case of legal heir
- If the claimant is minor, the guardian and relationship proof with the minor.
An employer can opt out of EDLI if it goes for a group term insurance cover with coverage equal or more than EDLI. There are several insurance companies which provide insurance to satisfy the requirement of EDLI. This is generally a flat coverage across all the employees and hence, the employee with lower pay gets the maximum benefit.
Share the article with the World.



