We are on the verge of completing another financial year 2017-18. We need to invest money to save on income taxes. Salaried persons have to submit their actual investments document to their employer. Employers will deduct taxes based on the provisions income tax act and submit to the Government of India according to the rule. Are you still left with some options which can save your money by reducing income tax? Read the following article Income Tax planning for salaried employees to explore all the ways of income tax deductions for salaried employees.
1. House Rent Allowance
House Rent Allowance (HRA) is the part of salary one gets from the employer. You can take benefit of income tax on the amount what you pay as house rent to your landlord. There is a rule how much of HRA you can claim as income tax benefit. First, you should satisfy the following conditions to get HRA as exempted from income tax.
- You must be a salaried individual. This is not applicable for self-employed individuals
- You get HRA as a part of your salary
- You pay rent regularly for your accommodation.
- The rent which you pay is more than 10% of the basic salary. Here basic salary means the Basic Pay + Dearness Allowance(DA)
You have to provide landlord’s PAN if you are paying rent over Rs 1 Lakh in a year to your landlord. You can provide a signed declaration in case the landlord does not have the PAN. If you are staying with your parent you can take HRA exemption for your HRA of salary. In this case, you need to provide the rent receipt from your parents. You cannot claim on income tax benefits if you pay rent to your spouse. You cannot claim the HRA benefit if you are staying in a self-owned house.
The HRA is exempted from the income which is the minimum of the followings.
- Rent Paid excess to the 10% of basic salary
- Actual HRA received from employer
- 50% of the basic salary for metro cities and 40% of the basic salary for Non-metro cities where the person resides.
HRA Calculation for Income Tax Benefit:
Suppose, Mr. A has Basic Pay of Rs 20,000 and DA of Rs 15,000 in his salary. He also gets HRA as Rs 15,000. He is paying rent of Rs 10,000 per month to his landlord and lives in Mumbai. According to the above three conditions, we have calculated the followings in chronological order.
- Rent paid – 10% of Basic Salary (Basic Pay + DA)=(10,000×12) – 10%(35000×12) = Rs 78,000
- Actual HRA received – 10,000×12 = Rs 1,20,000
- 50% of basic salary – Rs 2,10,000
Mr. A will get tax exemption for HRA of Rs 78,000 which is the minimum of the above calculation.
2. Medical Bills
An individual can get income tax benefit of up to Rs 15,000 in a financial year as medical allowance. You have to submit medical bills for Rs 15000. The medical expenses can be for self, spouse, children and dependent parents and siblings.
The employers are giving medical allowance in two ways.
The first way is the fixed medical allowance. Suppose your employer gives you Rs 15000 as medical allowance. You submit the bills for medical expenses of Rs 10,000. The balance Rs 5000 becomes taxable.
The second way is the medical reimbursement if your employer reimburses all your medical expenses. You submit the medical bill and the employer gives you the money. If all the claims are below Rs 15,000 you will get the income tax benefit on entire medical expenses. The balance amount is taxable in case of claiming more than Rs 15000 as medical expenses in a year.
These medical expenses can be for buying of medicines, laboratory bill, and treatment charges at hospitals, clinics etc.
It is the most neglected areas where individuals can save some tax. I have seen many people who are not organizing their medical bills regularly and face difficulties during submission of bills to their employer at the end. It is advised to keep your all medical bills at one place from the starting of the financial year and maintain an excel sheet to keep a record of those bills. It will definitely ease your task at the end of the year.
Download a sample excel sheet for MEDICAL BILLS to keep track of your all bills starting from a financial year.
3. Home Loan
The repayment towards a Home Loan is the great source of tax savings. You can claim the benefit on interest as well as principal part of the repayment amount.
Home loan interest is allowed to deduct from your income according to section 24 of income tax act. The maximum tax deduction allowed under section 24 is Rs 2 lakhs. This limit is for self-occupied property. If the property is not self-occupied there is no limit for tax benefit under section 24.
If the owner of the property is not residing in the self- property because of the profession, the tax deduction under section 24 shall be Rs 2 lakhs only.
This tax benefit is for completed property or the property which got the completion certificate or possession letter from the developer. If the property is under construction the deduction can be taken up to 5 years or completion of the project which is earlier.
The principal part of the repayment can be claimed as tax benefit under section 80C of income tax act. This deduction is allowed for a maximum of Rs 1.5 lakhs.
You can get the tax benefit of Rs 50,000 on the interest of home loan over and above Rs 2 lakh under section 80EE of income tax act. This deduction is allowed for the following cases.
- The value of the property should be less than Rs 50 Lakhs and the loan taken should be less than Rs 35 Lakhs.
- The loan should be sanctioned in the last financial year i.e. between 1st April 2016 and 31st March 2017.
- This benefit is available till the full repayment of the loan.
So total interest on housing loan deduction for AY 2018-19 is Rs 2.5 Lakhs.
4. Education Loan
The amount of interest paid towards repayment of education loan is eligible for tax benefit under the 80E provision of income tax. This deduction is available for individual tax-payers only.
There is no limit on the amount of deduction. The entire interest payment of education loan is tax-free. However, you cannot get any benefit on the principal amount of the loan.
You can avail the tax benefit when you actually pay the interest on education loan and the repayment should be from the income.
The education loan can be taken for the higher studies for self, spouse or children. You can also get the tax benefit for higher education of a student whose legal guardian is you.
5. Conveyance Allowance
Are you getting conveyance or transport allowance in your salary from your employer? You can save some money in income tax.
You can get the exemption of Rs 1600 per month or Rs 19,200 per year. This deduction is under section 10(14) of income tax.
You can get any amount from your employer as conveyance allowance but you will get the income tax benefit of maximum Rs 19,200 in a year because the conveyance allowance exemption limit is Rs 19,200 in the financial year 2017-18
You don’t have to submit any proof or bill to have the income tax benefit on conveyance allowance.
6. Mobile Expenses
Mobile allowance given by the employer is tax-free under section income tax act 10 (14).
There is no limit on allowances which can be exempted from income tax. The mobile is to be used for official purpose only.
Some employers take the declaration from an employee about the usage of their mobile calls whether it is official or personal.
7. Section 80C
You can claim tax benefit of up to Rs 1.5 Lakh under section 80C. This is the area where all tax-payers concentrate to take benefit to the fullest.
There are various instruments available by which you can save to get the benefit of tax savings. The investments on the followings are applicable in this section.
- Employee’s contribution to Employee Provident Fund (EPF)
- Public Provident Fund (PPF)
- Life Insurance Premium
- National Savings Certificate (NSC)
- Home Loan Principal
- Premium for Unit Linked Insurance Policies (ULIP)
- Equity Linked Savings Scheme (ELSS)
- Sukanya Samridhhi Yojana Account (SSY)
- Five years fixed deposit
- Senior Citizen Savings Scheme
- Children’s tuition fee
- Purchasing of annuity scheme of LIC or others
- Contribution to the selected pension funds
Also Read: Top 10 Best Income Tax Savings Options in AY 2018-19
If you deposit money in an annuity plan of LIC or any other insurer for pension funds you will get the tax benefit under section 80CC.
Salaried individuals can contribute to the NPS account under section 80CCD (1). The maximum deduction allowed in this contribution is 10% of the salary (Basic Pay + Dearness Allowance) up to Rs 1.5 lakhs.
Moreover, an employer’s contribution of up to 10% of basic salary can be exempted from income tax under section 80 CCD (2)
However, remember that the combined contribution towards 80C, 80CC, and 80CCD (1) is up to Rs 1.5 Lakhs.
To know more about tax planning, read another article ‘Tax Planning: Various Ways of Saving Income Tax’
8. Children Education Allowance
A fixed education allowance of Rs 100 per children for a maximum of 2 children is allowed as exemption from income tax. There is no requirement of bill to claim this exemption.
If the children reside in a hostel you can get maximum of Rs 300 per child as income tax benefit.
9. NPS
Under section 80C(1) you can get the tax benefit of Rs 1.5 lakhs. In addition to this, you can get the tax benefit of Rs 50,000 under section 80CCD (1b).
Hence if you invest Rs 2 lakhs in NPS you can have the entire benefit of income tax.
Also Read: Should you invest in NPS?
10. Health Insurance
Premium payment of medical or health insurance is exempted from income tax under section 80D of income tax act.
The maximum sum which can be claimed as income tax benefit s maximum Rs 15,000. The benefit is Rs 25,000 for medical insurance of senior citizens. The premium of the health insurance should be for you, your spouse, dependent children and parents.
11. Treatment of Serious Diseases
A deduction of maximum Rs 40,000 is tax exempted for medical treatment of self or dependents under section 80DDB. This deduction allows up to Rs 60,000 for the senior citizen. For very senior citizens the deduction allowed is Rs 80,000 in a financial year.
The medical treatment of diseases such as cancer, chronic renal failure, Parkinson and other specified diseases in the rule 11DD is allowed to be exempted. There is no need to take a certificate from a registered doctor in the Form-10. A self-declaration is now sufficient for the purpose.
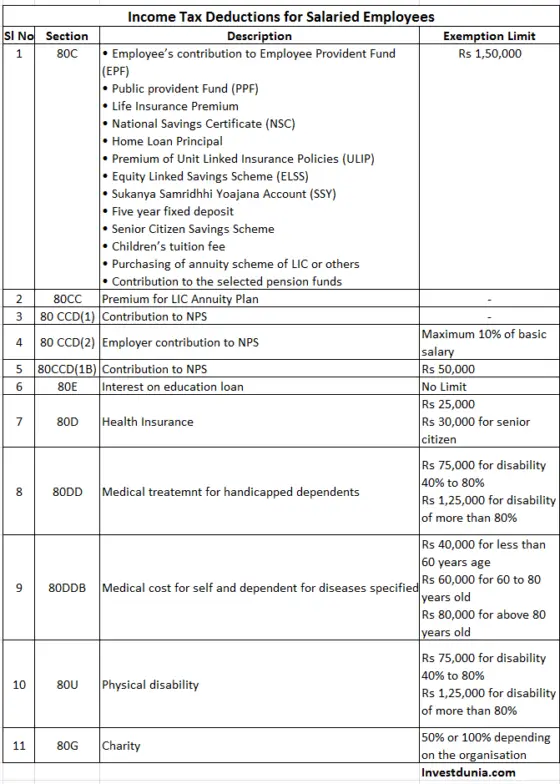
12. Handicapped Dependent
The expenditure incurred for the medical treatment of handicapped dependent is tax exempted under section 80DD of income tax act. The medical treatment costs include nursing and rehabilitation costs for the handicapped person.
There is a fixed amount which can be claimed as a tax benefit.
Disability between 40% and 80% – Rs 75,000 shall be exempted
Disability more than 80% – Rs 1,25,000 shall be exempted
For above 80% disability, a certificate of disability is required from prescribed medical authority. A certificate can be taken from a specialist from a govt or private hospital where the disabled person is being treated.
A deduction of Rs 75,000 and Rs 1,25,000 is also tax exempted for physical disability up to 80% and more than 80% respectively for an individual. This benefit is under section 80U of income tax.
13. Donations
Contributions made to charitable institutions or relief funds such as Prime Minister’s Relief Fund and chief minister’s relief fund are exempted from income tax under section 80G.
The deduction can be 50% or 100% of the contribution according to the organisation where you are contributing.
The contributions of more than Rs 2000 should not be made by cash. You cannot claim more than Rs 2000 as tax benefit if you have paid the fund by cash.
The employees have to claim the return according to the contribution while filling up the income tax return.
14. Income Tax Rebate
There is an income tax rebate of maximum Rs 2500 under section 87A. This rebate is allowed for the individuals whose total taxable income is Rs 3,50,000.
Here the taxable income means the gross income minus deductions under section 80C. The rebate is applicable for total tax before adding education cess. It is also available for senior citizens of 60 to 80 years age.
The rebate is applicable for Indian residents only. It cannot be allowed for NRIs.
Conclusion:
From the above article, you have understood how to save tax. If you are a salaried employee you should look each and every point by which you can save some taxes. List down all your investments and arrange them according to the type and submit those to your employer.
If you like the article share it with the world. 🙂